ECO-FRIENDLY STAMP TO YOUR END PRODUCT.





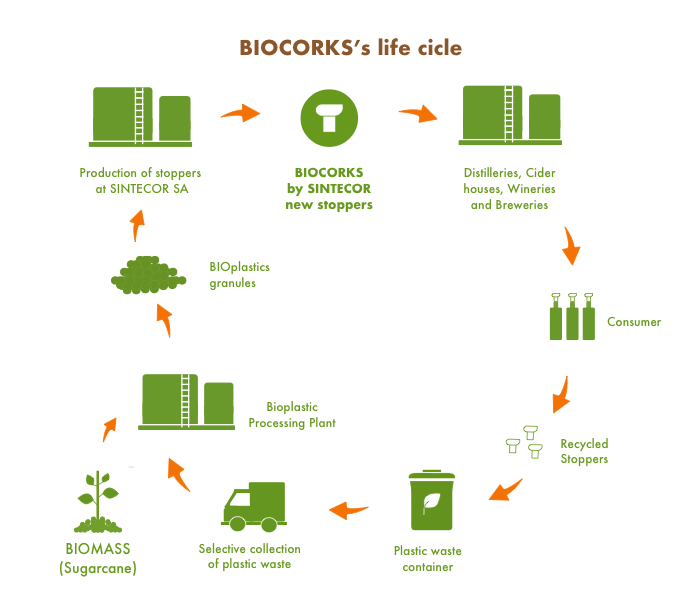
Biocorks are recyclable to contribute to the circular economy, and with a reverse carbon footprint. Yes! We capture CO2 from the environment.